How to start investing in Singapore? Beansprout's practical guide to get you started
By Beansprout • 01 Aug 2022 • 0 min read
Have you ever wondered how to start investing in Singapore? Here's our definitive step-by-step guide to get you started.
In this article
What you'll learn:
- Choosing an online investment platform
- Setting up your investment brokerage account
- Funding your investment brokerage account
- Buying and selling stocks
TL;DR
- For those wondering how to start investing in Singapore, the first question to answer is which investing platform to use.
- We would choose one based on having low fees and easy-to-navigate user interface.
- Apart from investing in stocks in Singapore, buying US stocks may also provide you with a chance to diversify their portfolios.
- Lastly, decide on a strategy before you start to invest. For example, you would need to think about whether your portfolio would consist only of Singapore stocks, or to also include stocks listed overseas.
Step 1: Choosing An Online Investing Platform
In order to get started, you need to select an online stockbroker to open an account. This online brokerage will serve as a platform for you to buy and sell stocks. Essentially, the brokerage functions as the middleman between you and the stock market by providing you access to various stock exchanges.
Although there are many brokerage platforms in Singapore to choose from, it is important for investors to pick the one that best suits their needs. For beginners who are new to investing, it is best to look for a low-cost broker with a relatively user-friendly interface.
All brokers will charge certain fees for their services, and this includes the commissions per trade on a percentage basis as well as conversion fees for different currencies.
Some brokers may also charge a minimum commission fee. For example, Saxo Markets’ SaxoTraderGo platform charges a minimum of US$4 commission for trading US stocks and S$5 commission for trading Singapore stocks.

Some of the fees to be aware of include:
- Commission fees: The brokerage firm will charge you a fee, usually a percentage of the total amount you buy/sell, for completing an order. There is also a minimum fee to be charged regardless of the size of your order. You may end up paying a huge proportion of your order as minimum fees if the order is very small.
- Forex rates: The broker will convert your non-USD denominated funds into USD at their own rates when you are buying the US equities. This will result in a fee collected for the service provided.
- Platform fees: Some brokerage firms will charge you a platform fee for using their trading platform. This fee may be waived, depending on the conditions set
- Dividend tax: The US taxes 30% of the dividends you receive if you are a non-US resident. This is in contrast to Singapore where your dividends are not taxed by the Singapore government.
For the purposes of this article, we will be demonstrating the process of setting up your brokerage account on Tiger Brokers.
Step 2: Setting Up Your Investment Brokerage Account
After signing up, you will need to complete an online identity verification process with your broker. This usually involves you submitting a copy of your NRIC or passport along with other relevant documents reflecting your full name and residential address.
Your broker may also conduct a customer knowledge assessment to determine the level of knowledge or experience you have in investing. While they might be a chore, these formalities are ultimately necessary for your broker to collect information as part of their ‘know your client’ verification checks for legal purposes.
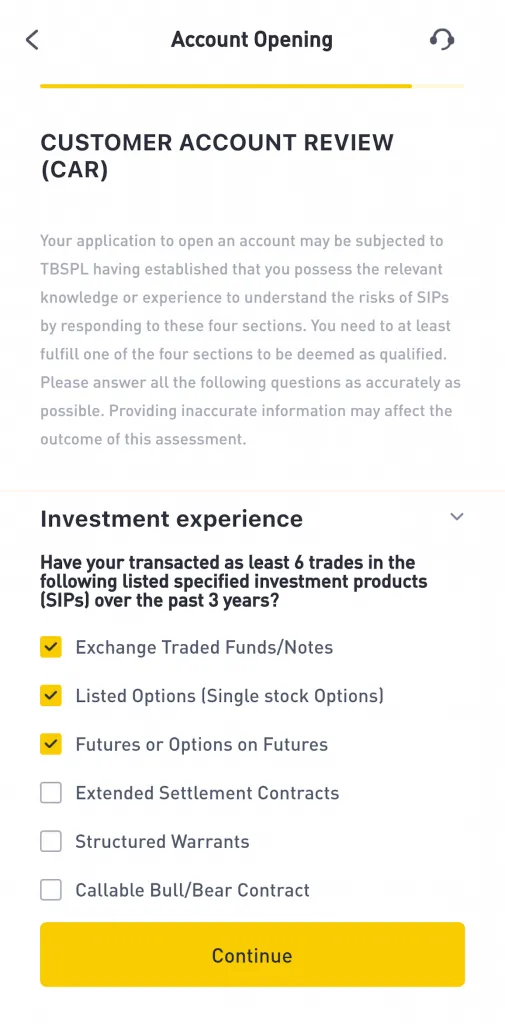
Source: Tiger Brokers
The process may look something like the image above, showing the Customer Account Review (CAR) checks being conducted by Tiger Brokers. Overall, these questions will also give you some understanding on how to invest in Singapore.
These checks have also been put in place to protect you from putting your money into riskier investment assets that you don’t understand. For that reason, all MAS-licensed brokers in Singapore are required to have these verification checks in place.
Step 3: Funding Your Investment Brokerage Account
Once you’ve finished setting up your online brokerage account, you will need to deposit funds into the account before purchasing investment assets. You can do it through several ways, which might include an online banking fast transfer, PayNow transfer, or wire transfer. Check to make sure that you are sending the right amount of money over, denominated in the correct currency!
Some brokerage platforms have a minimum deposit amount. TD Ameritrade, for example, requires a minimum funding of US$3,500. Tiger Brokers, however, has no minimum funding amount.
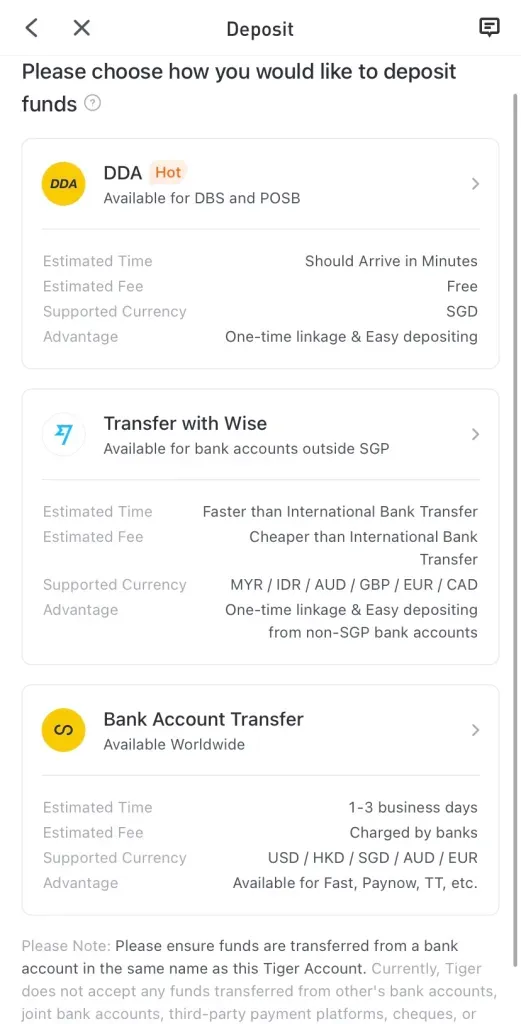
Source: Tiger Brokers
As shown above, Tiger Brokers allows you to deposit funds into your account in various ways, one of which is a Direct Debit Authorisation (DDA) with your DBS/POSB bank account. This is essentially a fast deposit service provided by DBS Bank.
Although you’re depositing the money into the trading platform, it does not mean that you will be investing all of it in one go. You can still choose when to buy your stocks at any given time.
Step 4: Buying And Selling Stocks
If you’re still wondering how to invest in Singapore with the funds from your account, you will need to learn about the actual step of buying stocks. Although it is not all that complicated, there are still a few things to take note of. For instance, there are different types of orders that your brokerage platform can execute.
As shown below, there are a number of orders that you can place. For simplicity’s sake, we will not be explaining every order type in this article.
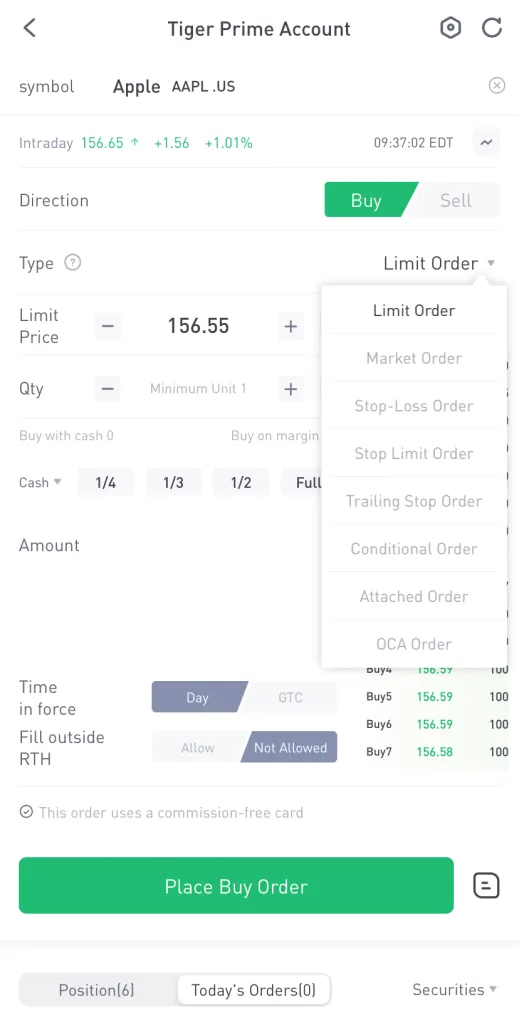
Source: Tiger Brokers
Broadly speaking, there are four common types of buy/sell orders that you can place on your online brokerage platform: (i) market order (ii) limit order (iii) stop-loss order (iv) trailing stop order.
a) Market Order
- This refers simply to executing the trade at the prevailing market price.
- In other words, if you set a market buy order for one Apple share, your trading platform will execute the trade at the current price.
b) Limit Order
- This involves choosing a specified price that you want to execute the trade at.
- For example, if you set a limit buy order for one Apple share at $160, it will only be executed if that price is met.
c) Stop-Loss Order
- This is an order meant to limit an investor’s downside on any given trade, by executing a buy or sell order once the stock has traded through a certain price.
- Imagine the price of Tesla stock drops from $900 to $800. If you have a stop-loss for Tesla set at $880, it will sell your stock at $880 and protect your position from dropping further.
d) Trailing Stop Order
- While similar to a stop-loss, this order is based on a given percentage change in the stock price rather than a specific price.
- Suppose you wish to sell Meta stock if the price drops 10%. If it climbs up to $300 then falls down to $200, your brokerage platform will sell at $270.

Step 5: Choose your investment strategy
You may feel the adrenaline rush as the funds settle in. There are a lot of exciting company names which you may have heard of such as DBS, Coca Cola, Mcdonalds, Apple etc. Take a deep breath! Before you rush to buy them, you should take a step back and think about your investment strategy.
For example one of the questions to answer is whether you should invest only in Singapore stocks, or to also invest in the US market.
The US market provides investors access to a wide range of stocks. Apart from familiar American companies such as Apple and Tesla, non-US companies such as Tencent, Alibaba, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing can be also be found listed on the US market
Investors can tap on the US market to gain access to both US and non-US companies and diversify their portfolio. This helps to reduce their portfolio risk as companies in different countries may react differently to the same event.
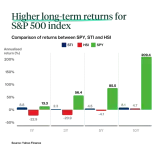
The US market as measured by the S&P 500 index has outperformed other stock indices in the long run, Despite events such as the 1929 Great Depression and 2008 Global Financial Crisis, the S&P 500 index has recovered to be trading at higher levels than pre-crisis.
What does it mean to short a stock?
When you short a stock, you are placing a bet against the stock or company, expecting the price to go down. Short selling is essentially a risky way to profit from a declining stock price.
This is the opposite of buying a stock and hoping that the price will go up, which is also referred to as opening a “long position” on the stock.
What does it mean to trade on margin?
Margin trading entails borrowing from the brokerage platform to purchase additional stock beyond what you can afford. The important thing to note is that margin trading carries serious risk and magnifies losses as much as it magnifies gains.
Margin trading is not designed for beginners, but experienced investors looking for additional leverage in their investment portfolio.
Take the next step
- Ready to start investing? Find out which Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) you can consider buying.
This article was first published on 01 August 2022 .
Gain financial insights in minutes
Subscribe to our free weekly newsletter for more insights to grow your wealth